Google Shopping Feed Optimisation – Have You Done These Seven Things?
In many eCommerce Google Ads accounts, Google Shopping is the most profitable part of the account. Many marketers will put in a lot of time and effort optimising what they can see within Google Ads but will often neglect an important aspect of a Shopping campaign — the feed!
A well optimised feed will help ensure that your products have a high relevancy for the search terms that are most relevant to them as well as helping to improve click-through rates. Additionally, a good feed will make it easier to create a good Shopping campaign structure.
While there are many factors that you can look at when optimising a feed. Here are seven areas that you can start looking into.
If you need help optimising your Google Shopping feed, visit our Google Shopping campaign page and get in touch to see how we can help.
1. Check the feed for mistakes
A basic starting point is to ensure that your feed does not have any mistakes in it. A spelling error in your ad can look unprofessional and may lead to the competitor winning the click instead of you.
Here are some things to look for:
- Spelling mistakes.
- Grammatical mistakes.
- Inconsistent use of capitalisation.
- Inconsistent information in the feed, such as the wrong colour mentioned in the description.
- Incorrect image.
- Incorrect delivery information.
- Incorrect price.
- Incorrect technical information in the description.
2. Optimise the Title
Aside from the image (and maybe the price), the title is arguably the next most prominent part of your ad that a user is going to see. This makes it a very important part of your ad to optimise.
The maximum character length for the title is 150 characters, but Google can truncate titles if they don’t fit in the space it allocates. So, make sure that your most important words are front weighted near the start of your title.
The title should have specific product information such as the brand, size, colour, material, gender etc.
Seeing as though adding in this information may lead to some of your titles being truncated, create a template title for all of your products and test to see which title order performs the best.
Here is an example order that you may choose for clothing products:
Brand > Gender > product type > colour > size > material
The order that you choose to add information in your title will differ depending on your niche and where you sit in your industry.
For example, if the brand that you sell isn’t a designer or highly desirable brand, you may choose not to put the brand at the front of the title.
If you’re selling a cheap brand, then you may decide that some other information is better placed at the front of the title.
On the other hand, if you specifically sell wedding clothes, then you may choose to add the word ‘wedding’ close to the start of the title.
This is because adding in ‘wedding’ will increase the likelihood that your ad shows for searches containing ‘wedding ‘. Also, ‘wedding’ being visible in the title will deter people who are not looking for wedding clothes, which will reduce wasted spend.
3. Optimise the image
The first part of your ad that most users will notice is the image. This makes it a very important part of your ad to optimise in order to increase your ad’s clickthrough rate. Here are some basic ways to optimise your images:
- Use high quality images — It goes without saying that you should use high-quality images.
- Image matches colour of product variant — make sure that the image matches the colour of the product. Don’t use a blue variant for all of the colour variants within a product for example.
Differentiate image to a competitor’s — Be creative and make your images different to your competitor’s images, especially if you sell the exact same product. This will help to make your ad stand out and may help to increase the clickthrough rate of your ad. You may choose to do this by showing your image in a different angle or switching between a lifestyle or non-lifestyle image.
4. Optimise the Product Description
Perhaps the least important suggestion in this list is to work on your descriptions. I like to make sure that the description contains all relevant information about the product that a user may find interesting if they wanted to find out more.
The maximum character length for a description is 5,000, but that doesn’t mean that you should write 5,000 characters. I would aim for around 500 to 750 characters. I don’t think people will be likely to want to read much more than that.
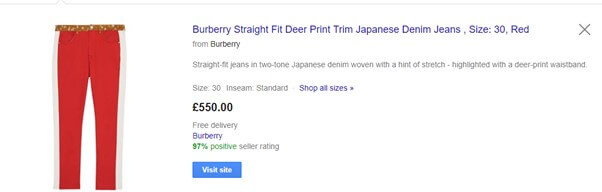
5. Use the right Google Product Category
Adding a Google Product Category doesn’t appear to be as important to get relevant results as it used to be, but it can still help. Despite it being an optional field in your feed, I would recommend adding a Google Product Category to all of your products.
A Google Product Category is not created by the marketer. Instead, Google has a set of product categories that you can choose from. You can find a list of all of the product categories that you can choose from in Google’s Product Taxonomy list.
When selecting a Google Product Category for each of your products, choose the most granular product category that is relevant to your product. So, for example, if you sell suits, then you may want to opt for the below Google Product Category for your products:
Apparel & Accessories > Clothing > Suits
However, keep an eye on the more granular google product categories. So, for any pantsuits, skirt suits, and tuxedos that you sell, Google has a product category that is a little more granular that you can use.

6. Improve your campaign structure with labels
Labels are an additional optional column that you can fully customise by adding whatever content you want. Each product can have up to four labels, which means you’re able to add four pieces of extra information with each product.
Google Ads allows for product and campaign structures to be segmented by label. This makes Labels a very powerful feature, allowing you to segment products in various ways so that you can bid differently on them. Here are some ideas on how you could choose to segment your products using labels so that you can bid differently on each particular segment:
- Sale and non-sale items.
- Price groups (e.g. all £1-£99 value products grouped together and all £100 – £199 value products grouped together).
- Best seller, average sellers and poor sellers — group products by how well they sell.
- Seasonal products — group products by the season that they sell well in.
- High, medium and low profit margin — group products by the extent of the profit margin.
7. Utilise Merchant Promotions
Part of optimising a feed is about putting your best message out there to entice as many of the right people as possible. If you have any discount codes or other offers, then you may be able to show them within your Shopping ad. Using Merchant Promotions helps to get your offers out there, which will most likely result in a higher clickthrough-rate and a higher conversion rate.
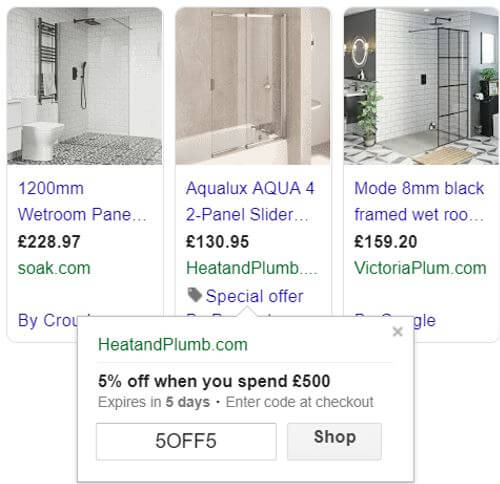
I find that discount codes on Merchant Promotions work well in niches that are highly discount oriented, like sofas and bathroom products.
I’ve also had success increasing the average order value by offering a discount to people who spend a certain amount above the client’s average order value.
If you don’t have Merchant Centre Promotions in your Google Merchant Centre, then you’ll need to request it. There are two ways to set up a promotion.
Simple promotions can be created using the promotions tool in Google Merchant Centre, but if you have a high number of promotions to submit, then you may find it useful to use a promotions feed.
Here are some examples of Merchant Centre promotions that you could try:
- Free delivery when you spend over a certain amount.
- Free gift with every purchase of a particular product.
- A percentage discount off all goods or a specific set of goods with a discount code.
- A monetary discount off all goods or a specific set of goods with a discount code.